Inhaltsverzeichnis
Past perfect
Simple form
Event in the past perfect before another past event
The past perfect shows that an event in the past happened before another event in the past.
(1) Lisa couldn’t pay. She had forgotten her purse.
(2) When Peter arrived, Sue had already left the bar.
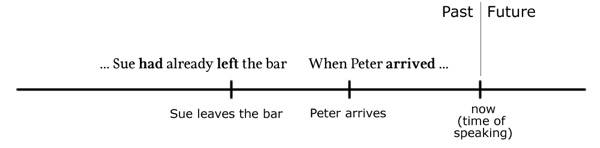
Past state [Zustand] before a past event
(3) She had known him for years when he told her that he was gay.
(4) When I visited John in the hospital, he had been there for three months.
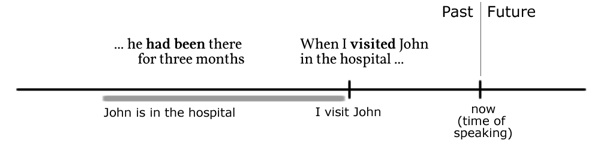
Comparison: past perfect ⟷ past tense
Past perfect
(5) When Roy’s girlfriend arrived he had cooked the dinner.
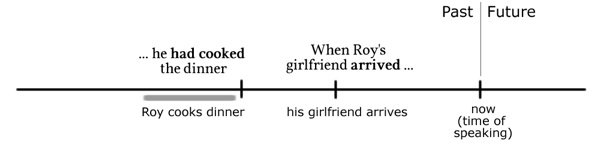
The dinner is ready when she arrives.
Past tense
(6) When Roy’s girlfriend arrived he cooked the dinner.
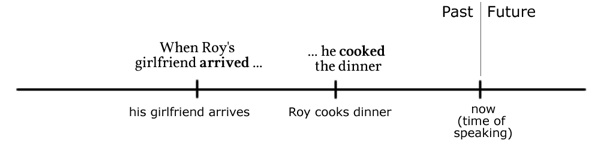
He starts cooking the dinner after she arrives.
Progressive form
The past perfect progressive is used much like the simple form but you use it if you want to stress [betonen] the duration [Dauer] of the event in the past perfect or if it’s important to say how long it had been going on when the other past event happened.
(7) When Roy’s girlfriend arrived he had been cooking dinner for three hours.
(8) Tom had been dreaming about doing a bungee jump for years when he finally decided to do it.
